Illness Impacting Milk Production

A multitude of chronic diseases or new onset illness can impact mom and breastmilk production in the postpartum period. Risk factors for low production of breastmilk include infertility, diabetes, thyroid disease, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), obesity, and high blood pressure.
However, this list is not comprehensive. Unfortunately, we see patients more frequently with “idiopathic” low production – i.e. we have no explanation for why it occurs. There are theories that this may be related to “endocrine disrupters” (i.e environment) that impact the cells in the breast. Others point to the potential role of “early menarche” (a woman getting her period very young, as this may impact the breast from developing fully).
These cases are heartbreaking for moms, and it is so important to assess mom’s mental health and support her in what works for her. While moms most moms will state their goal is “to feed the baby at the breast without supplementation,” this is unfortunately not always a reality. However, some moms with moderate milk production may be able to gradually increase their production over several months with the use of galactagogues (herbs and medications that increase production) and other targeted interventions. Every case is individual and should be addressed as such. What is “do-able” for a mom at 2 weeks may not be “do-able” at one month, so I have frequent visits with patients until we are at a stable baseline and continue to reassess plan, changing course if necessary.
Chronic Health Conditions
If you have a history of autoimmune or neurologic disease, or have received an organ transplant, you should seek prenatal consult regarding breastfeeding. Most immune-modulating medications are safe with breastfeeding, but should be explored individually with your physicians.
If you or your child require hospitalization for any illness or procedure, the Academy of Breastfeeding Medicine has a new protocol on Supporting Breastfeeding During Maternal or Child Hospitalization that provides excellent guidance for hospital systems and patients regarding lactation.
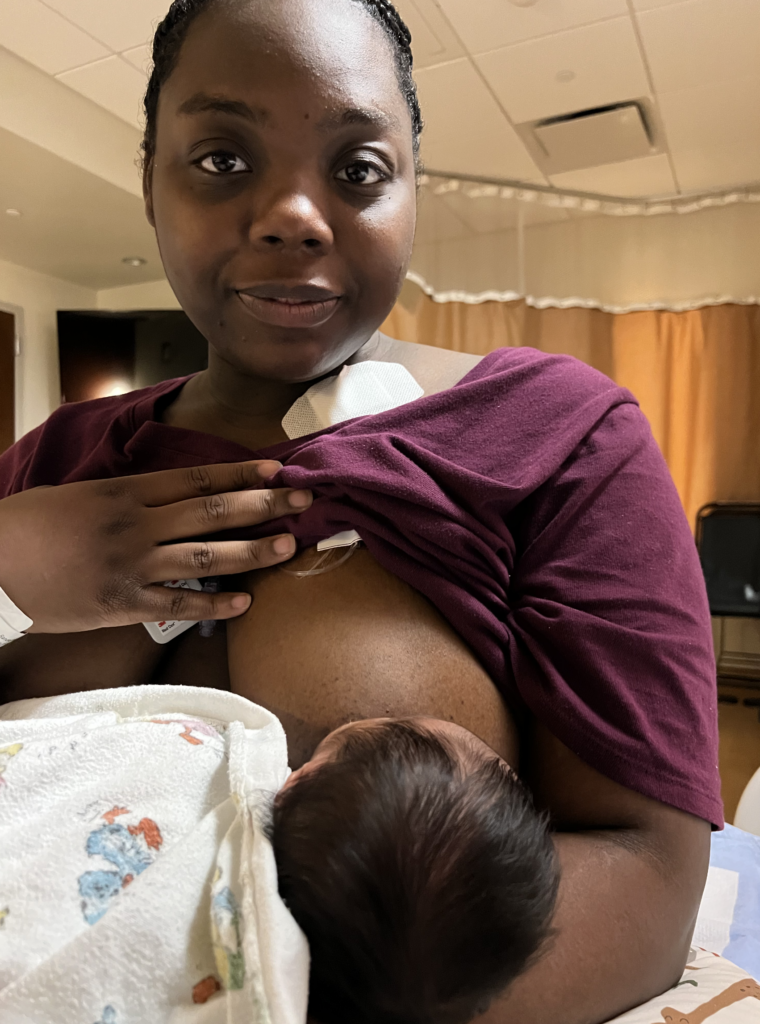
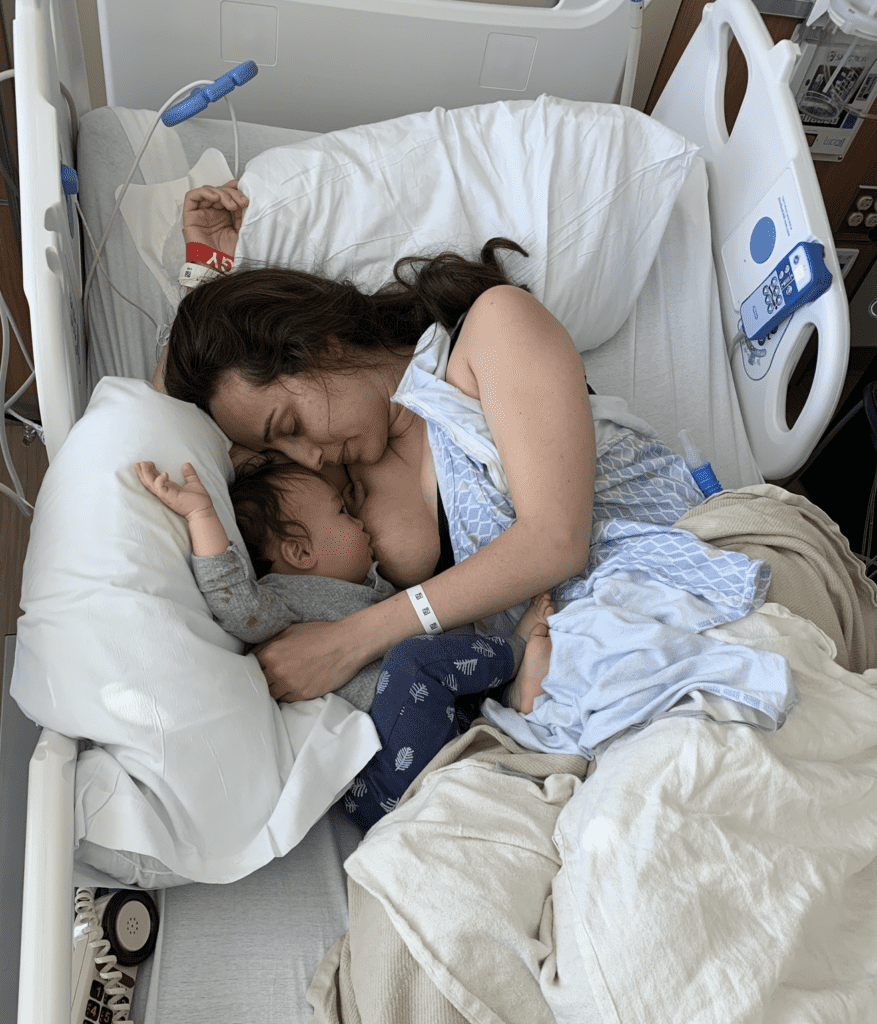

This mother unfortunately was diagnosed with lymphoma two days postpartum when she was experiencing chest pain and a CT scan showed a large mass near her lungs and heart. She had a port placement to start urgent chemotherapy. She was able to feed her newborn breastmilk until chemotherapy started, but unfortunately had to wean after that. Chemotherapy is one of the few medication regimens that is not safe with breastfeeding.
Breastfeeding While Pregnant or Undergoing IVF
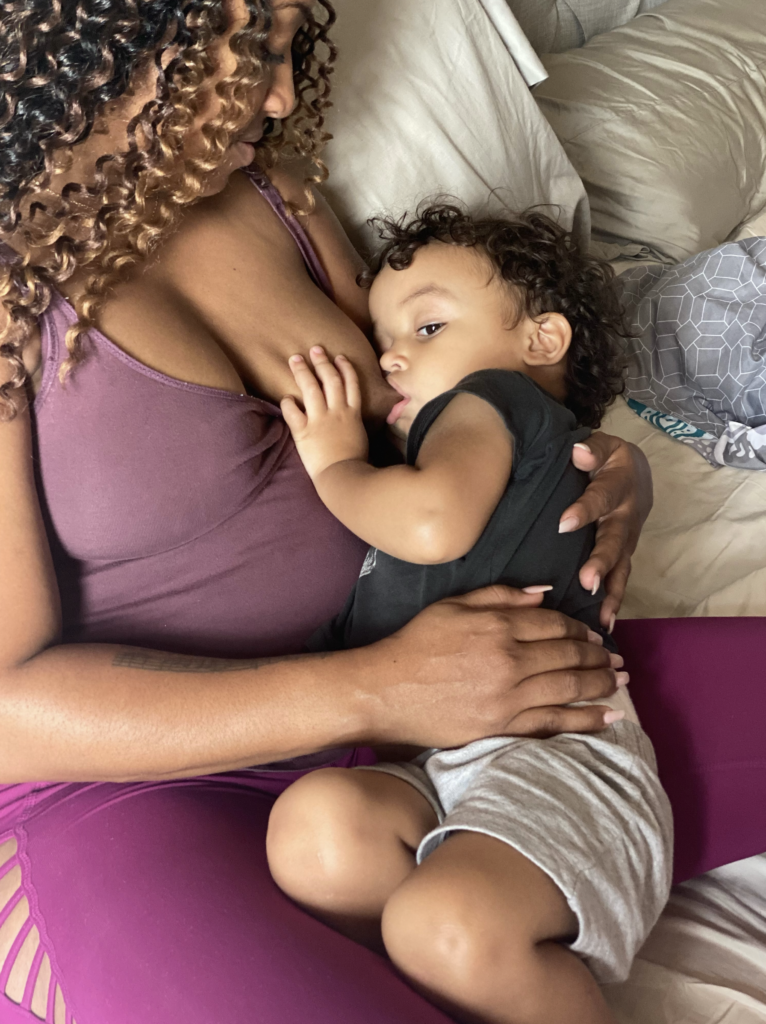

There is no evidence to suggest that breastfeeding while pregnant is harmful to the fetus, increases miscarriage risk, or contributes to preterm labor.
Many women who are undergoing IVF are advised to stop breastfeeding. While many women become pregnant while breastfeeding and doing IVF treatments, the reproductive endocrinologists do not have good data related to this and so they will be conservative and request patients stop breastfeeding. When patients are not ready to stop breastfeeding at one year, I ask them if another six months will make any difference in their lives or fertility. The answer most often is no. So I recommend they continue breastfeeding for another six months and reevaluate then, if their doctor mandates cessation of breastfeeding.
In addition, lack of ideal birth spacing has an adverse impact on maternal and infant morbidity and mortality, including low birth weight, preterm birth, uterine rupture. ACOG advises against new pregnancy before six months postpartum and ideally recommends at least 18 months duration between one birth and new conception.
Exercise, Weight Loss, and Nutrition
Exercise and reasonable weight loss are safe with breastfeeding. Weight loss supplements that involve herbs and stimulants should be avoided. Exercise and weight loss will not impact your breastmilk production. Even in situations of starvation, the body will protect the milk production (at the expense of mom’s own nutrition, if severe). Always be wary of anecdotal reports from friends and/or the internet describing a drop in milk production with exercise. Remember that decreases in milk production are most often multifactorial, including decreasing breastfeeding or pumping time, sleep training, start of hormonal contraception, and return of menses. Breastfeeding mothers do require additional calories based on whether they are exclusively breastfeeding or supplementing, and should eat a healthy and balanced diet during lactation.



Wrist and Neck Pain
If you are experiencing wrist and/or neck pain with breastfeeding, please seek evaluation by a professional! This means you are hunching and hand expressing in unideal positions and should work through alternative options.
Flus, Colds, Covid
Once you demonstrate symptoms from an illness, your baby has already been exposed. We do not recommend separating yourself from your infant or pumping breastmilk instead of feeding baby at the breast. The exception to this rule is herpes simplex virus (which causes cold sores and genital sores and can occur on the nipple as well) or shingles (varicella, or the chicken pox virus). These viruses do in fact pose a danger from contact of the infant or child to the affected breast. The milk from the affected breast should be pumped and discarded until lesions scab over, and that breast kept covered. The child can feed from the unaffected breast.

The Covid vaccine is safe during breastfeeding. If you have a Covid exposure, you should not stop breastfeeding. In fact, a study recently published in the Lancet on maternal-infant feeding and separation policies showed, using the Lives Saved Tool, the number of infant deaths in low-income and middle-income countries due to COVID-19 (2020–21) might range between 1800 to 2800. By contrast, if mothers with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were recommended to separate from their newborn babies and avoid or stop breastfeeding, additional deaths among infants would range between 188,000 to 273 000.
Vaccines
Tattoos
It is safe to undergo a tattooing procedure while breastfeeding, though you should take care to ensure normal precautions with needle safety are observed.
Injectables and Herbs
The strict answer to herbs and injectables/fillers such as Botox are that we “do not have data in breastfeeding.” However, given the local mechanism of action of injectables/fillers, there is no reason why would enter the bloodstream nor be excreted in breastmilk. Further, Botox is being used for infant conditions such as neonatal spasticity and Hirschsprung’s Disease.
When a patient has a choice of an herb or a prescription medication, I encourage patients to use prescription medication for which we have data and well-established drug information. For example, if a patient is suffering from postpartum depression, I would encourage her to use a prescription medication treatment rather than herbal.
However, most of the galactagogues (substances that increase milk production) we have used for hundreds of years in lactation do not actually have robust data regarding safety. Therefore, patients should speak with their physicians regarding individual decision making.
Recreational Drugs and Alcohol
Substances of abuse such as cocaine, methamphetamines, and hallucinogens are not safe with breastfeeding. Marijuana, which has high excretion in breastmilk and concentrates in fat, is not safe in pregnancy or breastfeeding; infants brains are largely comprised of fat.
Alcohol metabolism in breastmilk is identical to that of the blood. If you nurse an infant, have a glass of wine, and then nurse the infant three hours later, this is safe as you would also be safe to drive a car. However, if you are impaired in any way that driving or any other activity would not be safe, breastfeeding is also not safe!

Environmental Exposures
While concern sometimes arises over environmental exposures in in household cleaning items or beauty products, there is no evidence to suggest that breastmilk is contaminated. The risks of not breastfeeding generally outweigh all theoretical risks of possible harm. Women with silicone breast implants may question the safety in breastfeeding. Ironically, the silicone levels in cow’s milk and formula are exponentially higher than that of breast milk. Further, we use silicone in commercial over-the-counter products like simethicone to reduce gas and colic. Breastfeeding is safe with silicone breast implants.
Lopsided Breasts
Moms may unconsciously favor one breast or may be told to relieve engorgement from one “overactive” breast by pumping it or continually feeding the baby on it. This unfortunately just worsens the imbalance, as the breast that is “behind” will be less and less stimulated, and the overstimulated breast will become more stimulated by more feeding.

An easy way to maintain equal production (and breast size) is to always feed the baby off the less full breast first. This allows the overproducing side to remain full and therefore downregulate, and it tells the breast producing less to “perk up.” Contrary to traditional lactation lore, there is no risk to leaving a breast full. Mastitis results from imbalance in the breast microbiome, overproduction of milk, and non-physiologic removal of milk such as pumps that cannot mimic an infant’s mouth.
Based on differences in breast glandular density and receptor-level responsiveness to stimulation, you may find that you ultimately feed off both breasts evenly. Or you may find one breast is less full in say a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio compared to the other breast.
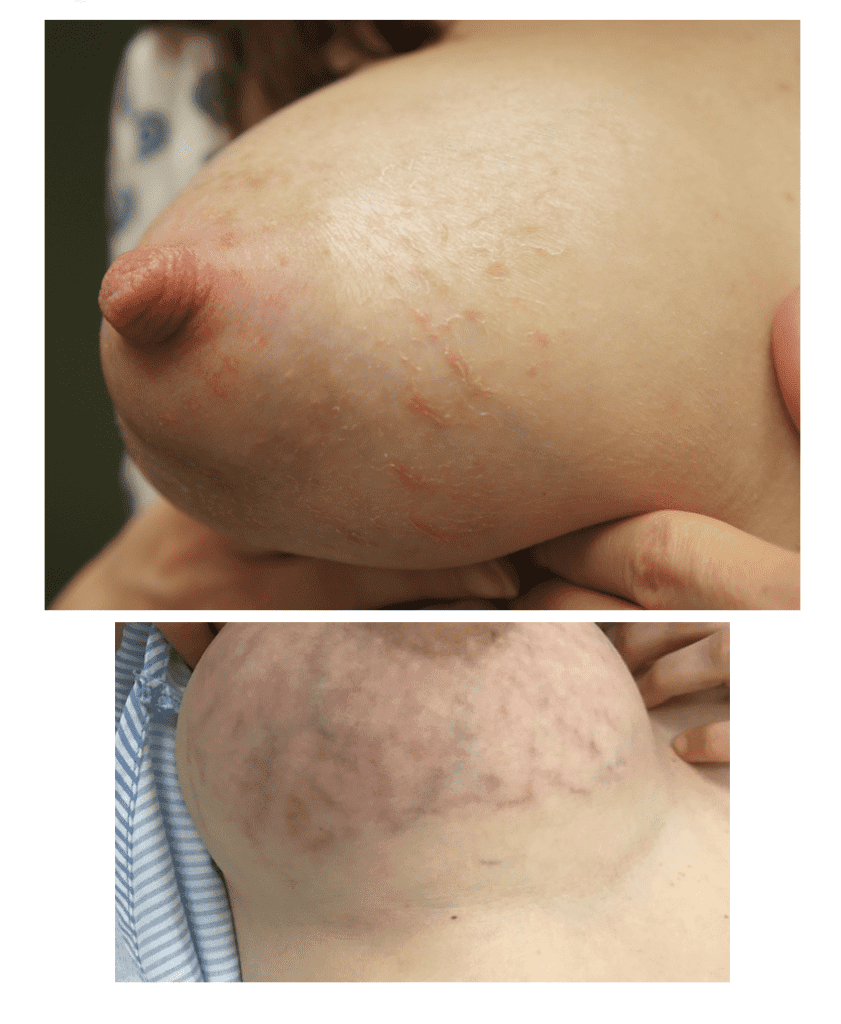
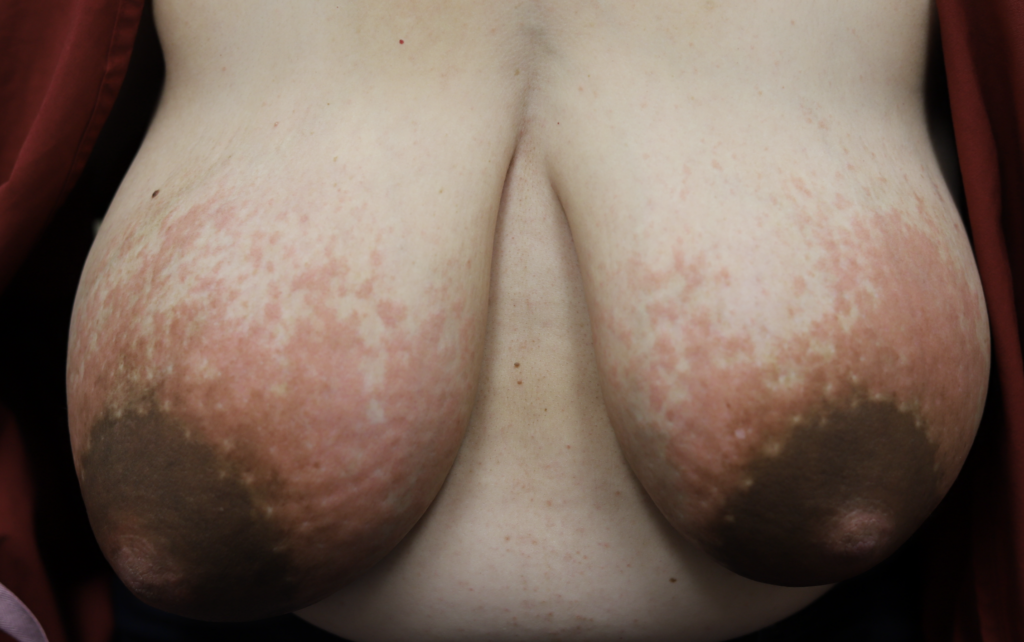
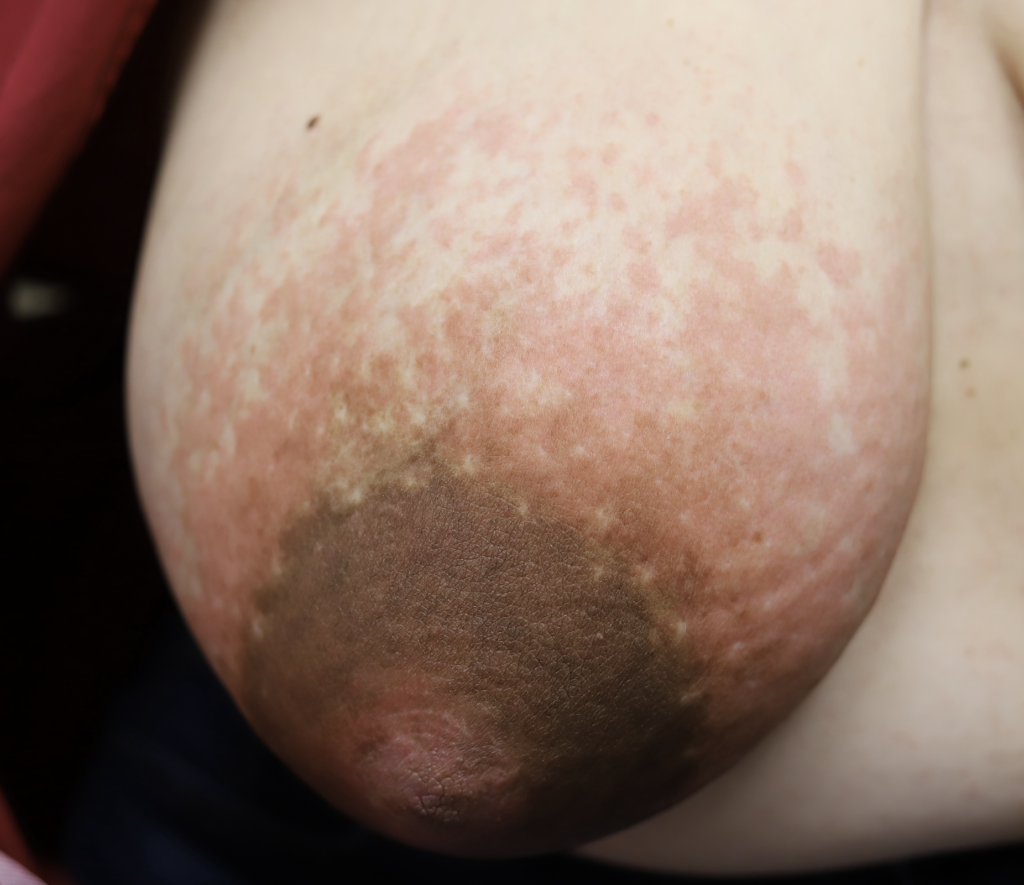
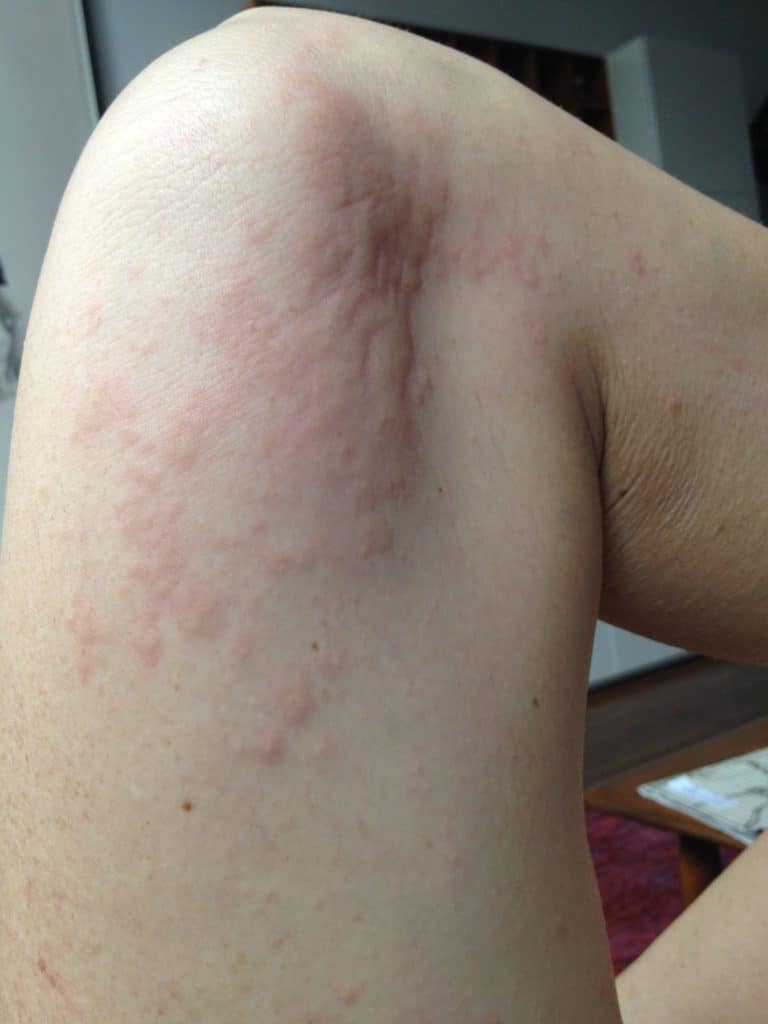
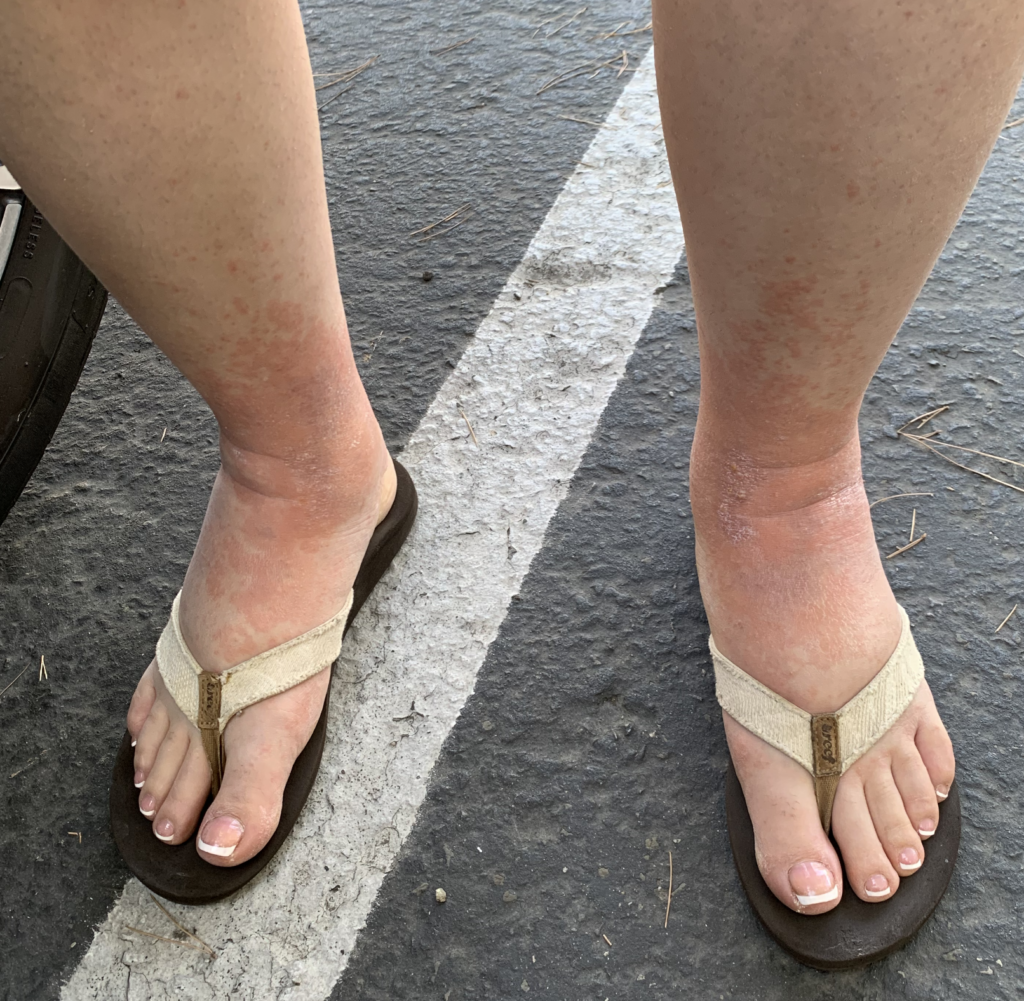
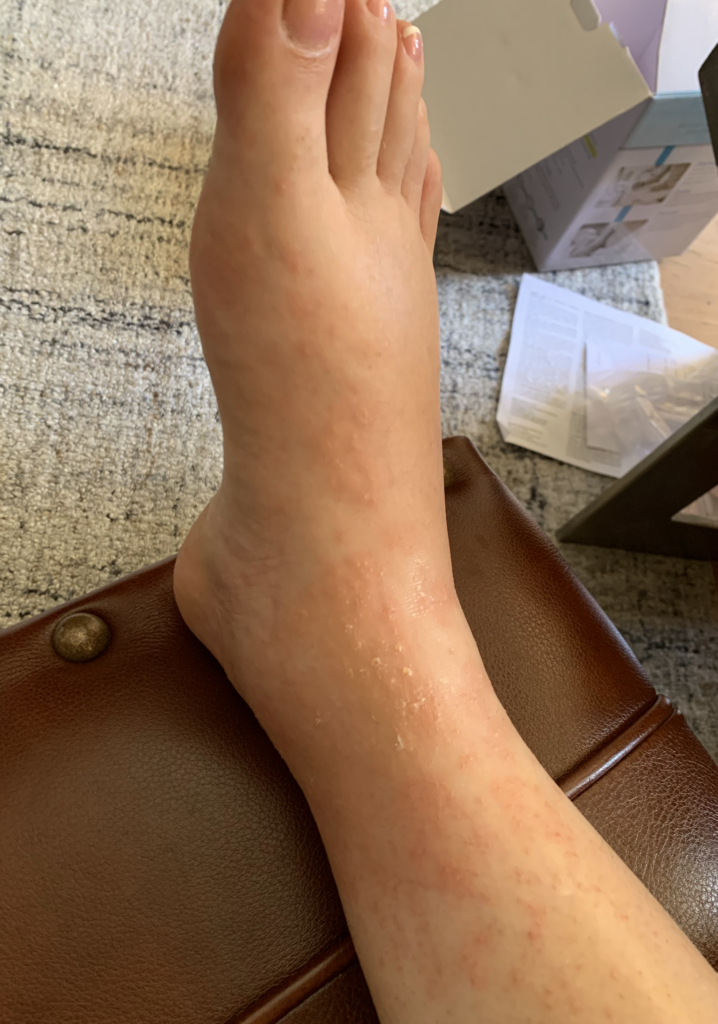
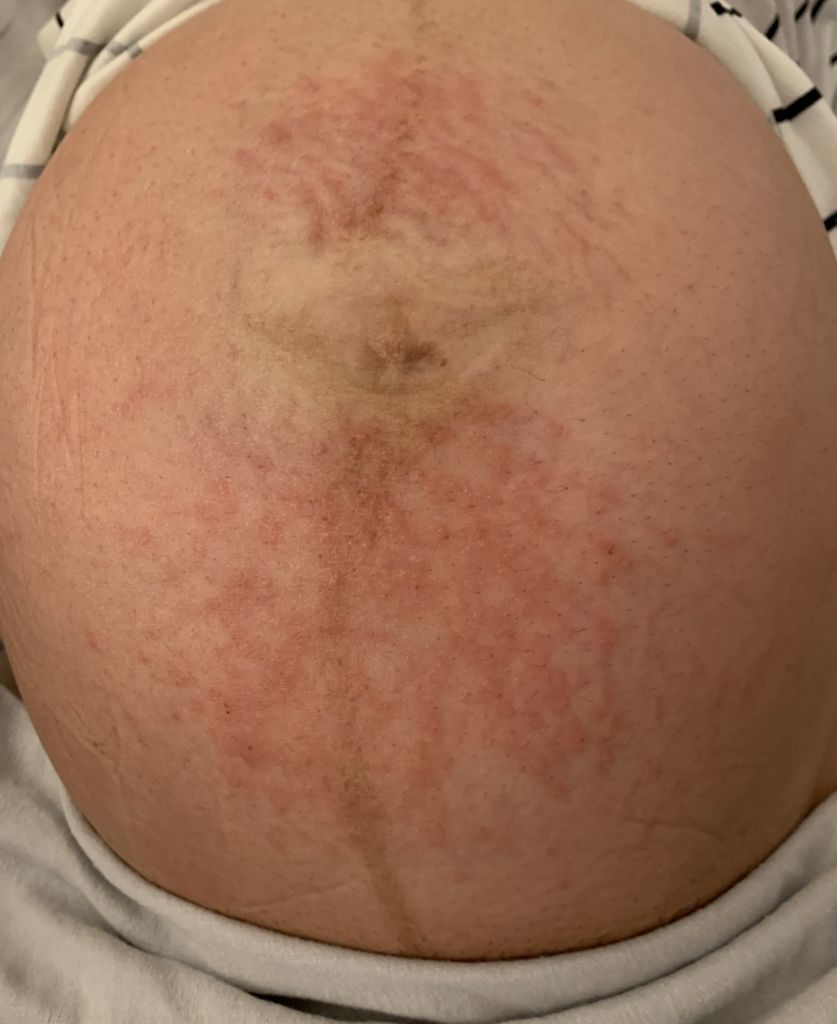
PUPPP and HIVES
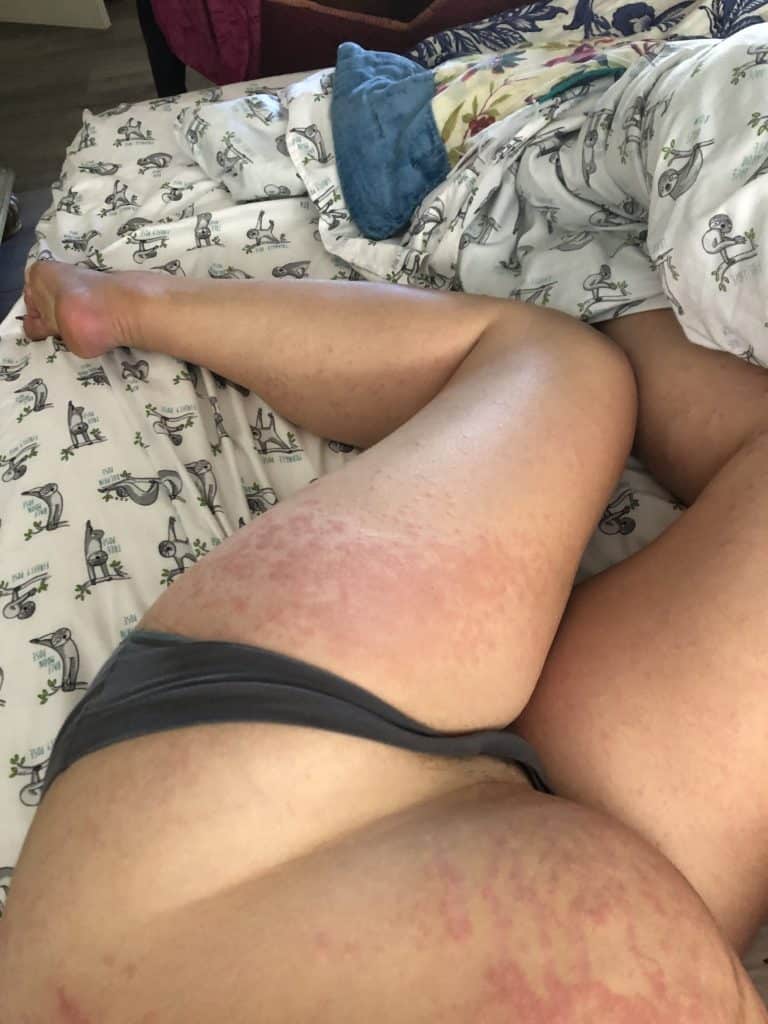
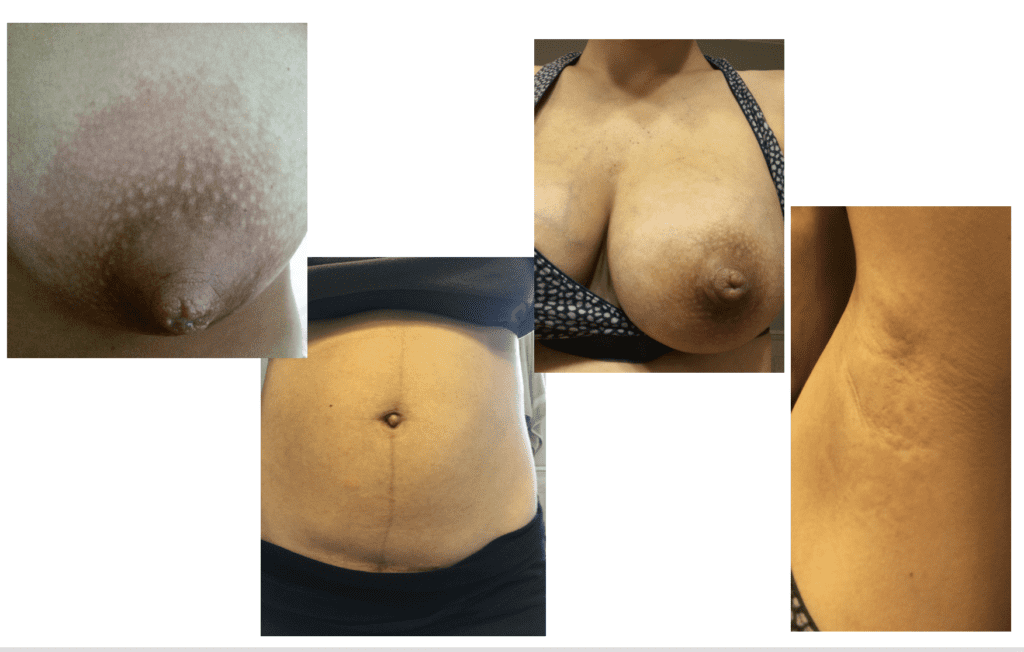
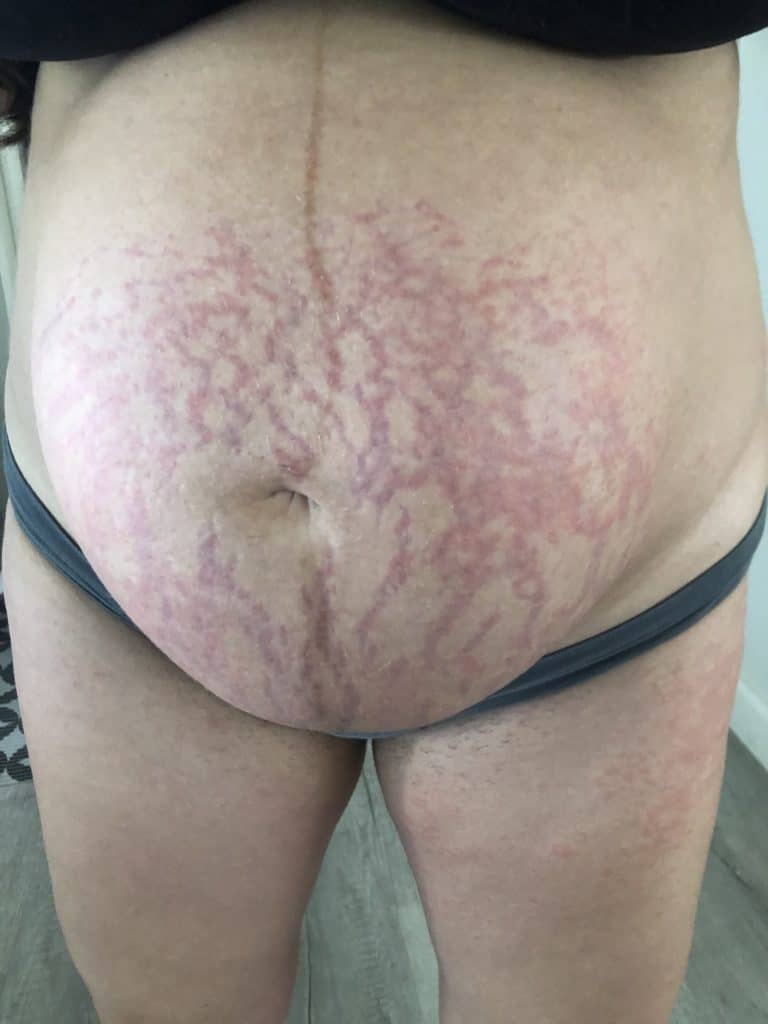
PUPPP (Pruritic Urticarial Plaques and Papules of Pregnancy), a benign (non-cancerous) disorder that causes inflammation and itching of the skin mainly in abdominal or breast stretch marks, can be excruciating for patients.
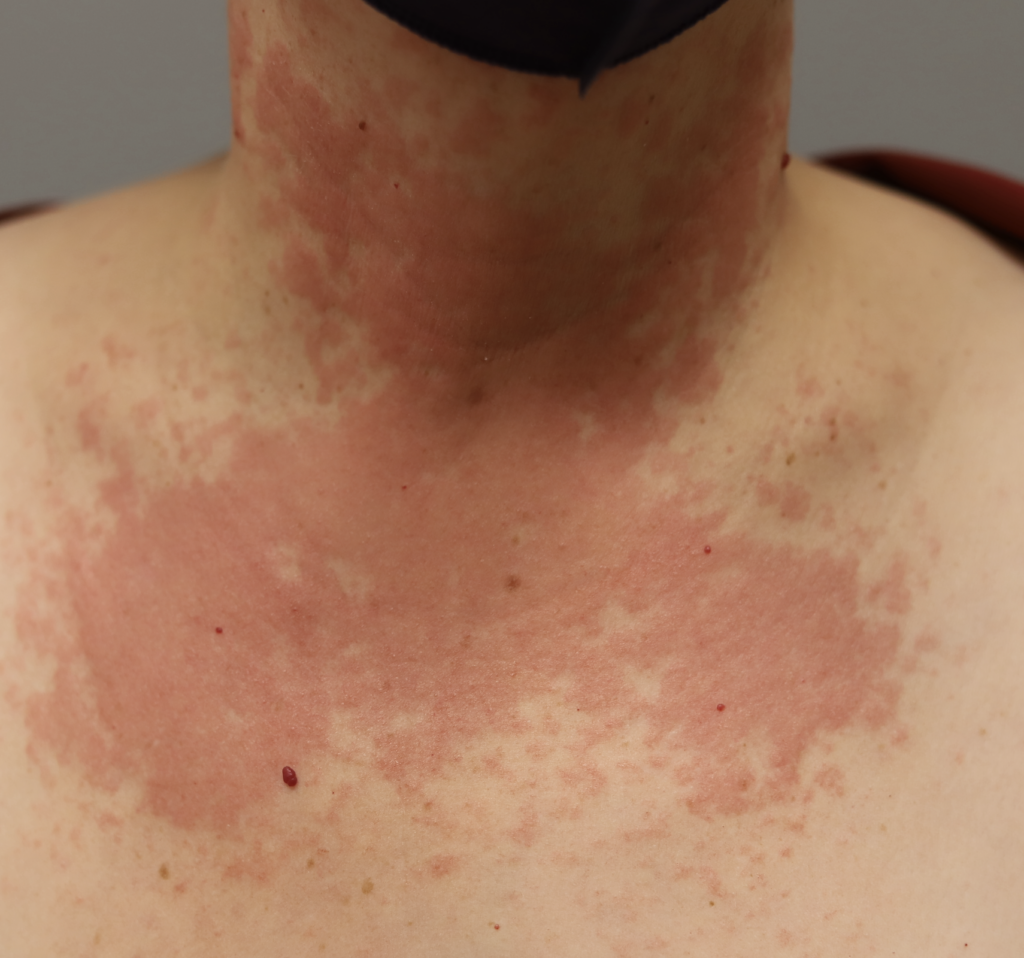
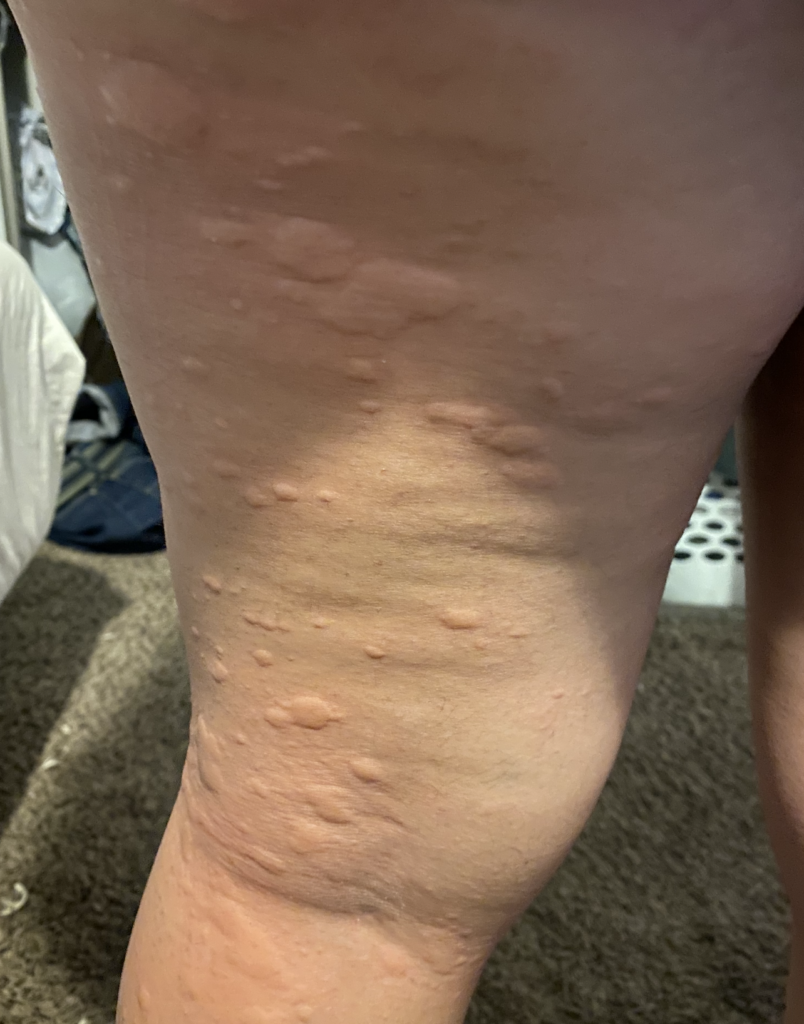
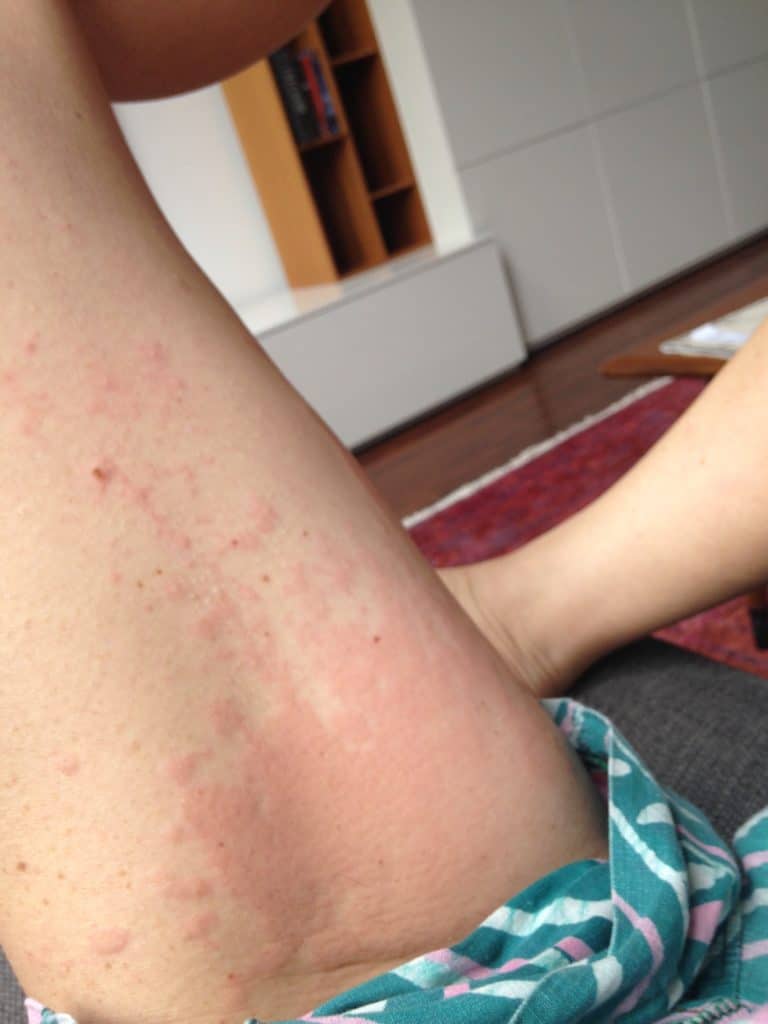
Hives may start in a small patch of tissue where mom contacts something she is allergic to. However, once mast cells (reactive cells that live in skin) become activated with itching, hives can spread rapidly. They may become cyclical, worsening at night or when a woman is hot. They occur most frequently under the arm, the groin, the scalp, and the backs of knees and elbows.
Idiopathic (meaning we don’t know why it occurs) hives are not uncommon in pregnant or postpartum women. Hives worsen with anxiety and it can become a vicious cycle of flares. Moms may not improve despite steroid or allergy creams, or allergy and/or steroid medications by mouth (which also can decrease milk production as well as cause excessive sleepiness or insomnia). I have found acupuncture treatment to be extremely effective in eliminating the cycle of hive flares. Moms usually need just one or two treatments to completely clear.